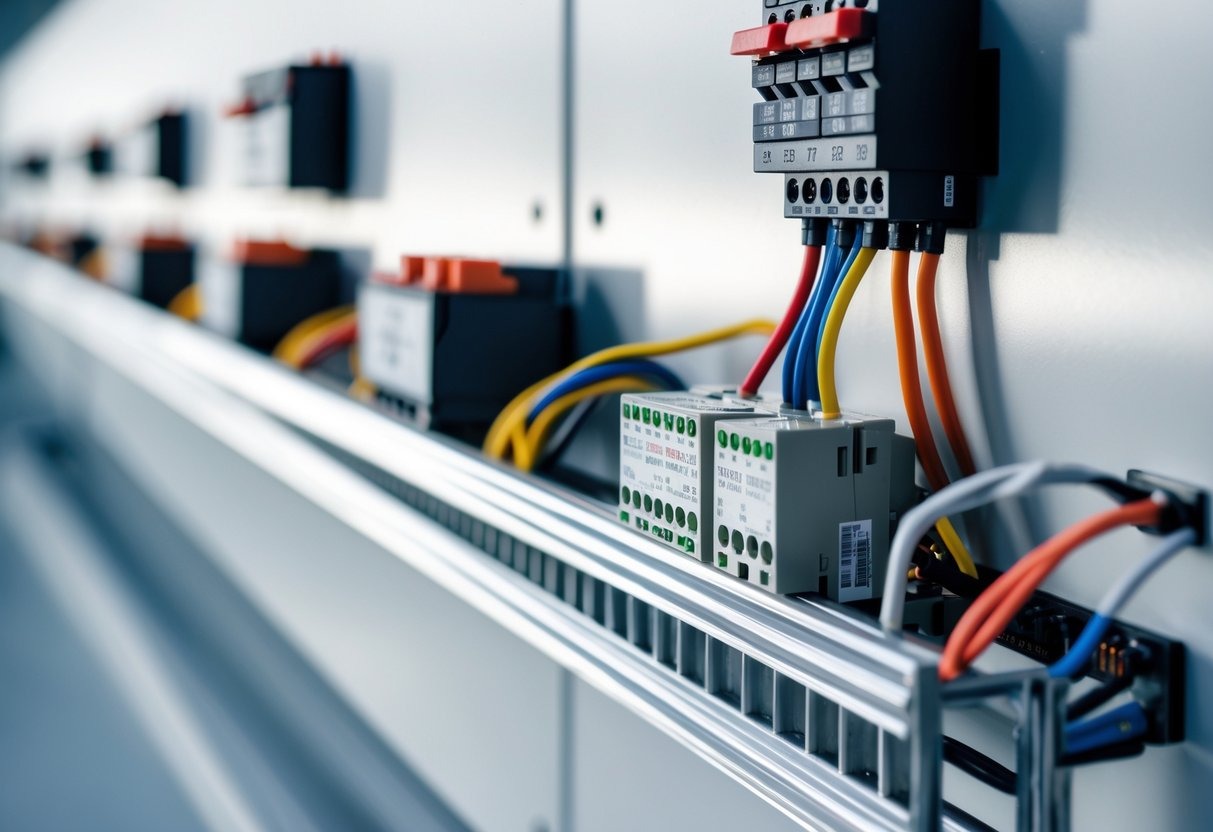
DIN rails are essential components in the realm of electrical installations. They are standardized metal strips used for mounting various types of electrical equipment securely within enclosures, ensuring organization and space efficiency. With a simple design, DIN rails support items like circuit breakers, power supplies, and controllers, making them a backbone of modern electrical cabinets.
These versatile rails come in various types, including Top Hat, Mini Top Hat, C-Rails, and G-Rails, each serving different needs based on size and application. Understanding the characteristics of each type enables better choices in both design and functionality. DIN rails not only streamline installations but also simplify maintenance, keeping everything in one organized place.
Exploring the basics of DIN rails is crucial for anyone involved in electrical projects. With the right knowledge, one can enhance the performance and safety of electrical systems.
Defining DIN Rails

DIN rails are essential components in electrical installations that provide a standardized way to mount various devices. Understanding their meaning, history, and applications helps to appreciate their importance in modern electrical systems.
DIN Rail Meaning and Standardization
A DIN rail is a metal strip, typically made of steel or aluminum, used to securely mount electrical components in cabinets. The term “DIN” stands for Deutsches Institut für Normung, which means “German Institute for Standardization.” This organization established a set of standards for the design and dimensions of these rails.
DIN rails ensure compatibility among various components, allowing devices like circuit breakers, relays, and terminal blocks to be easily attached. There are different types of DIN rails, including Top Hat, Mini Top Hat, C-Rails, and G-Rails, each designed for specific applications and loads. This standardization helps simplify installation and maintenance while promoting uniformity across industries.
History and Development of DIN Rails
The history of DIN rails began in the late 1920s in Germany when the lack of standardization in electrical installations posed a problem. Rheinisch-Westfälisches Elektrizitätswerk first developed the G-rail to address this issue, enabling safer and more organized installations.
In the early 1950s, DIN adopted the designs and further refined the specifications, leading to wider acceptance of the standard. As electrical components and systems evolved, DIN rails became a global standard, embraced by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) in the USA. Today, DIN rails play a crucial role in how electrical equipment is mounted and accessed, maintaining safety and compliance in various industries.
Where DIN Rails Are Used
DIN rails are used in a variety of applications, primarily within electrical enclosures. They provide a secure mounting solution for essential components such as:
- Circuit Breakers
- Relays
- Power Supplies
- Terminal Blocks
These rails are commonly found in settings like industrial control panels, commercial buildings, and residential wiring systems. Their versatility allows for both compact and larger installations, optimizing space while ensuring easy access for maintenance. By standardizing equipment layout, DIN rails facilitate quick upgrades or replacements, contributing to efficient electrical system management.
DIN Rail Basics
DIN rails are essential in electrical installations, serving as standardized support structures for mounting various electrical components. They provide organization and ensure compatibility across different manufacturers and devices. Understanding their materials, installation processes, and standard dimensions can help in selecting the right type for any project.
Common Materials and Finishes
DIN rails are typically made from metals such as steel, aluminum, or sometimes plastic.
- Steel is the most common material due to its strength and durability.
- Aluminum offers lightweight benefits while still providing good support.
- Plastic versions are used in low-load applications.
The finish on these rails is often galvanized or painted to prevent rust and corrosion. This ensures longevity, especially in harsh environments. Selecting the right material based on the specific application can improve performance and reliability in installations.
Mounting and Installation Process
Installing DIN rails is a straightforward process. First, the location must be determined based on the layout of the electrical components and available space.
- Preparation: Gather necessary tools such as screws, drill, and level.
- Alignment: Position the rail horizontally or vertically, ensuring it’s level.
- Fixing: Secure the rail to the mounting surface using appropriate screws or bolts.
DIN rails can be attached directly to enclosures or panels. They can also accommodate snap-on components, allowing for easy upgrades or replacements. Proper installation is vital for maintaining electrical safety and ensuring efficient operation.
Standard Dimensions and Profiles
DIN rails come in various standard dimensions to fit different requirements. The most common types include:
- TS35: A 35mm wide rail is the most widely used and versatile option.
- TS15: A narrower 15mm version, ideal for compact spaces.
- G-Rails: These are 32mm wide and provide robust support for heavier components.
The channel depths can vary as well, typically ranging from 5.5mm to 15mm. Each profile type has its designated use, making it crucial to choose the right one based on the application requirements. This standardization allows for universal compatibility across devices and manufacturers.
Types of DIN Rails
DIN rails come in various types, each designed for specific applications and equipment mounting. Understanding these types can help in choosing the right rail for various electrical projects.
Top Hat (Type TH) DIN Rails
Top Hat DIN rails, also known as TS35, are the most popular type. They measure 35mm wide and are versatile for mounting electrical components like circuit breakers and relays.
The cross-section resembles a “hat,” allowing for easy attachment of devices. These rails can handle a range of equipment sizes and weights, which makes them ideal for general electrical installations. Their standard depth is 7.5mm, with a deeper option of 15mm available.
Installation is straightforward and efficient. Components can slide or snap into place without major adjustments, facilitating faster setups. This design helps optimize space and keep installations organized.
C-Section DIN Rails
C-Section DIN rails have a 32mm width and feature a C-shaped cross-section. These rails are preferred for mounting heavier components like transformers and power supplies.
The sturdy design provides excellent support and stability, making them suitable for demanding applications. They allow for secure attachment, reducing the risk of equipment displacement.
While less common than Top Hat rails, C-Section DIN rails remain valuable in scenarios requiring robust support. Their unique shape does not only provide strength but also ease of use in various settings, making them appealing for professionals in the electrical field.
G-Section DIN Rails
G-Section DIN rails, known as TS32, are designed with a deeper cavity at one end. They measure 32mm in width and offer additional depth for mounting heavier components.
This design prevents accidental backward installation, ensuring that components stay securely in place. G-Section rails are ideal for applications needing extra support, like heavy-duty motors or controllers.
These rails are often used in industrial settings where components face more stress and load. The added robustness aids in maintaining the integrity of electrical systems, making G-Section rails a reliable choice for many users.
Applications of DIN Rails
DIN rails have versatile applications across various industries, providing essential support for mounting electrical components. Their standardized design simplifies installations, enhances safety, and improves efficiency in numerous settings.
Industrial Automation
In industrial automation, DIN rails are crucial for organizing and securing components such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs), relays, and terminal blocks. These rails streamline the setup of control panels in factories, helping to manage numerous electrical devices in a compact space.
DIN rails also allow for easy maintenance and upgrades. Technicians can quickly replace or rearrange components without specialized tools, reducing downtime. Commonly used in manufacturing, robotics, and chemical processing, DIN rails support a reliable and efficient workflow.
Electrical Panel Building
DIN rails serve as the backbone of electrical panel building, where they mount vital devices like miniature circuit breakers and surge protection devices. Their standardized dimensions ensure compatibility between various components, making panel assembly straightforward.
This modular approach allows for organized layouts, aiding in troubleshooting and maintenance. By providing clear separation between live and neutral components, DIN rails enhance safety within electrical enclosures. They are widely used in both residential and commercial electrical systems.
HVAC Controls
In HVAC controls, DIN rails are increasingly essential for mounting timers, contactors, and monitoring devices. Their reliable structure supports various temperature control units efficiently.
The use of DIN rails helps create organized control panels, critical for managing HVAC systems. Easy access to components boosts maintenance efficiency and minimizes service delays. As HVAC technology evolves, DIN rails continue to provide a reliable solution for professionals in managing complex climate control systems.
Choosing the Right DIN Rail
Selecting the correct DIN rail is critical for safe and efficient electrical installations. Gabby electric emphasizes the importance of matching rail types with existing components and considering the environmental conditions where they will be used.
Compatibility and Load Requirements
When choosing a DIN rail, ensuring it matches the components designed for it is vital. The standard types, like TS35, typically accommodate various devices, including circuit breakers and relays.
Load requirements also play a significant role. Heavier components may need a stronger profile. For instance, the G-section rail is ideal for heavier loads. The choice of a material, such as steel or aluminum, can also affect load-bearing capacity.
Factors to evaluate:
- Component Weight: Consider the total weight to avoid rail failure.
- Size of Components: Larger devices may require more space.
- Number of Devices: High-density layouts can require specific mounting solutions.
Environmental Considerations
Environmental conditions greatly influence the choice of DIN rail. Factors like temperature, humidity, and exposure to chemicals can affect performance and durability.
Material selection is influenced by the environment:
- Zinc-Plated Steel: Good for indoor use but may rust in damp areas.
- Aluminum: Lightweight and resistant to corrosion, suitable for moderate conditions.
- Stainless Steel: Best for harsh conditions, resistant to moisture and chemicals, but more expensive.
Key questions to consider:
- Will it encounter moisture or corrosive substances?
- Is it exposed to extreme temperatures?
- Will vibrations and shocks be present?
By evaluating these conditions, it is possible to select the most suitable DIN rail for the application.