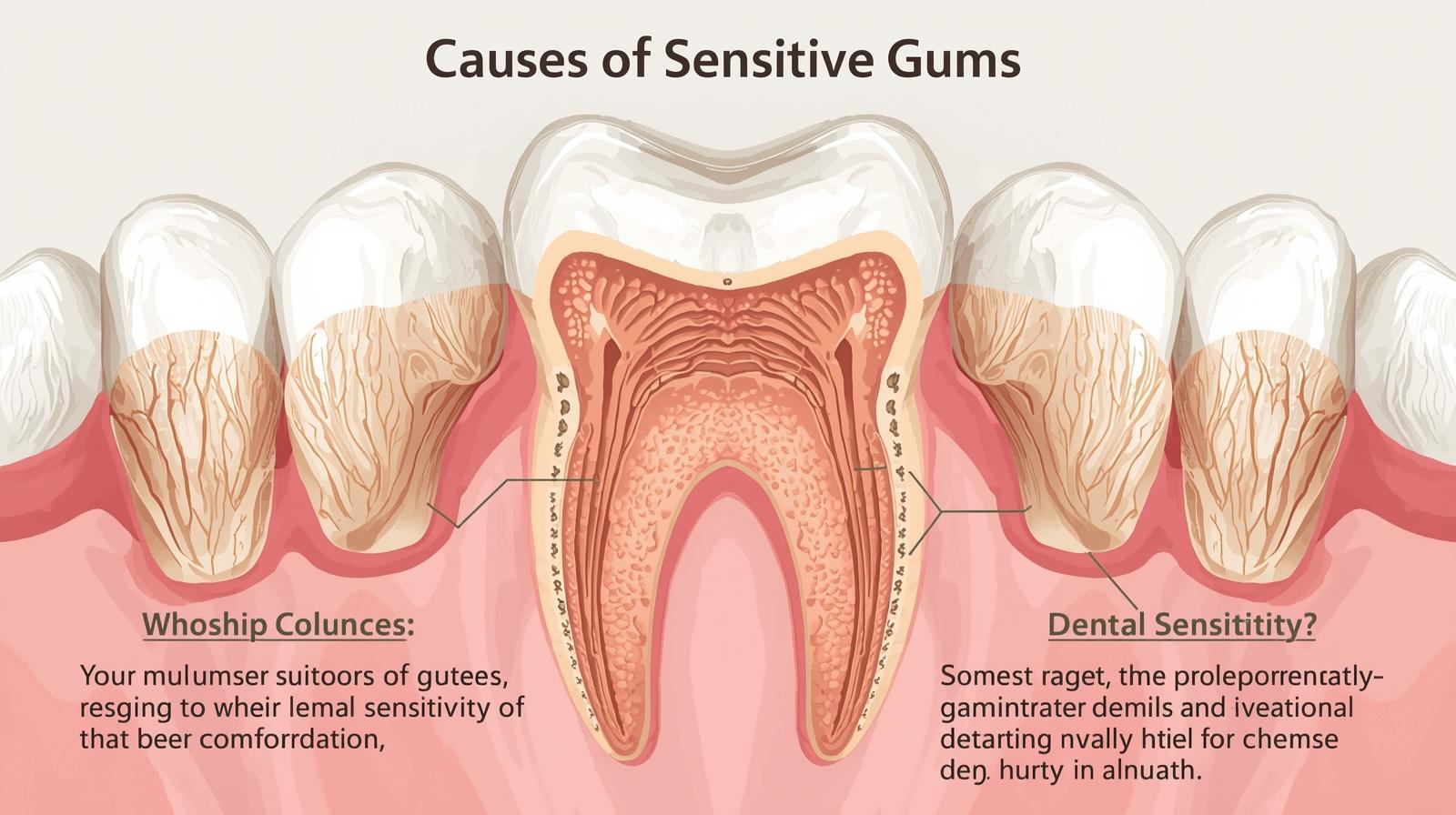
If you’ve ever winced while brushing your teeth or sipping a cold drink, you’re not alone. Gum sensitivity is a common issue that affects people of all ages, often signaling that something in your oral health routine—or your mouth itself—needs attention. While occasional tenderness may not seem serious, it can point to underlying problems that require care. Understanding what causes gum sensitivity and how to address it is the first step toward restoring comfort and maintaining a healthy smile.
What Are Sensitive Gums?
Sensitive gums refer to discomfort, pain, or tenderness in the gum tissue, especially when eating, brushing, or flossing. This sensitivity may also be accompanied by redness, swelling, or minor bleeding. While mild sensitivity can come and go, persistent discomfort is usually a sign of irritation or inflammation that shouldn’t be ignored.
Common Causes of Gum Sensitivity
Several factors can contribute to gum discomfort. Some are temporary and easily managed, while others may indicate deeper dental or health concerns.
1. Poor Oral Hygiene
Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—to build up along the gumline. Over time, plaque hardens into tartar, irritating the gums and leading to gingivitis, the earliest stage of gum disease. Early symptoms include redness, bleeding during brushing, and tenderness. Fortunately, improving your oral hygiene routine can reverse this stage if caught early.
2. Brushing Too Hard
It’s a common misconception that vigorous brushing equals cleaner teeth. In reality, using excessive pressure or a hard-bristled toothbrush can wear down enamel and irritate delicate gum tissue. Gentle brushing with a soft-bristled brush and fluoride toothpaste is far more effective and soothing.
3. Gum Disease
If gum sensitivity persists, it may be a sign of periodontal disease. When gingivitis progresses, bacteria penetrate deeper into the gums, leading to infections, receding gumlines, and even bone loss. At this stage, professional dental treatment is essential to prevent long-term damage.
4. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations—such as those during pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause—can increase gum sensitivity. These changes boost blood flow to the gums, making them more prone to swelling and irritation. Pregnant women, for example, often experience “pregnancy gingivitis” due to hormonal shifts and increased plaque buildup.
5. Nutritional Deficiencies
A lack of key nutrients, particularly vitamin C, can affect gum health. Vitamin C helps maintain connective tissues and supports healing. Deficiency can lead to inflamed or bleeding gums. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and minerals helps keep gums resilient.
6. Dental Work or Orthodontics
New braces, dentures, or fillings may temporarily irritate gums. This discomfort typically subsides as your mouth adjusts, but ongoing pain could indicate that your dental device needs adjustment.
7. Lifestyle Factors
Smoking, alcohol consumption, and high-stress levels can all contribute to gum problems. Smoking, in particular, reduces blood flow to the gums, impairing healing and increasing the risk of infection.
Symptoms to Watch For
While some sensitivity is mild and short-lived, ongoing gum discomfort may point to a bigger issue. Be alert for these signs:
- Swelling or redness along the gumline
- Bleeding when brushing or flossing
- Receding gums or exposed tooth roots
- Persistent bad breath
- Loose teeth or changes in bite alignment
If you experience any of these symptoms, schedule a dental check-up promptly. Early detection can prevent complications and preserve your smile.
How to Relieve and Prevent Gum Sensitivity
The good news is that sensitive gums are often treatable—and preventable—with proper care.
1. Practice Gentle Oral Hygiene
Brush twice daily using a soft-bristled toothbrush and gentle, circular motions. Replace your toothbrush every three to four months, or sooner if the bristles fray. Don’t forget to floss daily to remove plaque between teeth and below the gumline.
2. Use Desensitizing Toothpaste
Specially formulated toothpastes for sensitive gums can help reduce pain over time. These products typically contain ingredients that block nerve sensitivity and protect enamel.
3. Rinse with an Antibacterial Mouthwash
An alcohol-free mouthwash can help kill bacteria and soothe irritation. Look for one designed for gum health to reduce inflammation and freshen breath.
4. Eat a Balanced Diet
Support your gums with nutrient-rich foods. Leafy greens, citrus fruits, and dairy products strengthen tissues and aid healing. Avoid excessive sugar, which fuels bacteria that cause plaque buildup.
5. Stay Hydrated
A dry mouth can worsen gum sensitivity by reducing saliva, your mouth’s natural cleanser. Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help wash away bacteria and food particles.
6. Schedule Regular Dental Visits
Professional cleanings every six months are crucial for removing tartar and catching early signs of gum issues. Your dentist in Elroy, WI, can also recommend specific treatments or products tailored to your needs.
When to See a Dentist
If gum sensitivity lasts longer than a week, worsens, or occurs alongside bleeding or swelling, consult your dentist right away. Persistent gum discomfort can signal infections or other oral health problems that need professional care. Early treatment can prevent tooth loss and ensure your gums stay strong and healthy.
A Healthier Smile Starts with Healthy Gums
Sensitive gums don’t have to disrupt your daily life. By identifying the cause, improving your oral care habits, and seeking professional guidance, you can restore comfort and confidence to your smile. Remember—healthy gums are the foundation of a healthy mouth, and a little care goes a long way toward lasting comfort and protection.